NEUROLOGY
Neurology is the field of studying Structure, diseases and function of nervous system which includes spinal cord, Brain and Nerves. It deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of disease and disorders involving the central and peripheral nervous system. The nervous system is a sophisticated and complex system which controls and coordinates body activities normally.
NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
A Neurological disorder is any disorder of Nervous System. Neurological disorders can be categorized according to the primary location affected, the primary type of dysfunction involved, or the primary type of cause. The broadest division is between central nervous system disorders and peripheral nervous system disorders. Abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves like Structural, biochemical or electrical can result as symptoms sometime
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
The central nervous system (CNS) is made up of the brain, the spinal cord, and the optic nerves. The central nervous system controls thought processes, guides movement, and registers sensations throughout the body. Brain and Spinal cord are the core parts of the CNS. CNS is responsible for all involuntary actions. The CNS is often divided into white and gray matter. CNS support cells, called glial cells, outnumber neurons 10 to 1.
NEUROSURGERY
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery is the medical specialty focused on the prevention, diagnosis, and rehabilitation of disorders which affect any part of the nervous system such as the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and extra-cranial cerebrovascular system. They help in the diagnosis of intracerebral haemorrhage.
NEURO-ONCOLOGY
Neuro-oncology is the study of brain and spinal cord neoplasms, many of which are dangerous and life threatening. The global incidence of brain tumour is higher than 45/100,000 patients a year. According to National brain tumour society, there are about 120 types of brain tumour. The widely known type of brain tumour is glioma that originates from glial tissues. Meningioma is the most common type of spinal cord tumour which originates from CNS. The treatment given for neurological tumours is based upon the type of tumour, position in the spine and the age of the patient.
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
Neurophysiology is a branch of physiology and neuroscience that is concerned with the study of the functioning of the nervous system. These studies are carried out using electrophysiological or molecular biological tools. Discussions can also be made in neuromuscular physiology, neural mechanisms of higher nervous activity and contemporary problems of Neuroscience can also be conferred.
NEUROIMMUNOLOGY
Neuroimmunology is a field combining neuroscience, the study of the nervous system, and immunology, the study of the immune system. Neuroimmunologists seek to better understand the interactions of these nervous system and immunology during development, homeostasis, and response to injuries.
STROKE
A stroke is a "brain attack". It can happen to anyone at any time. It occurs when blood flow to an area of brain is cut off. When this happens, brain cells are deprived of oxygen and begin to die. When brain cells die during a stroke, abilities controlled by that area of the brain such as memory and muscle control are lost.
CEREBROSPINAL COMPLICATIONS
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) secures the brain and spinal cord. CSF spills happen through a correspondence between the covering of the Brain and the nose. These correspondences may happen suddenly or result from injury or earlier sinonasal surgery. Entanglements may happen if the reason is surgery or injury. Diseases after surgery or injury can prompt meningitis and genuine intricacies, for example, swelling of the Brain.
ADDICTION & BRAIN DISORDERS
Addiction is Brain Disorder and its complex condition. Addiction directly affects the function of brain and body which will result in problems in families, relationship, friends, schools, workplaces and neighbourhoods. Addiction can be prevented, treated and managed by the healthcare professionals with the co-operation of family or peer support like social worker.
PARKINSON’S DISEASE
Parkinson's disease is a progressive nervous system disorder that affects movement. Symptoms start gradually, sometimes starting with a barely noticeable tremor in just one hand. Tremors are common, but the disorder also commonly causes stiffness or slowing of movement. Later on rearranging stride is watched. Indications incorporate uneasiness, dejection and dementia. It is caused by an absence of dopamine. It is likewise called as hypokinetic unbending disorder, loss of motion gaits. In many people, Parkinson's ailment is idiopathic.
PAEDIATRIC NEUROLOGY
Paediatric Neurology is a mix of both Neurology and Paediatrics. A medicinal expert who represents considerable authority in this field of paediatric neurology is called pediatric neurologists.A paediatric neurologist is a doctor with expertise in diagnosing and managing the vast range of neurological disorders affecting children and young people.
NEURODEGENERATIVE DISORDERS
Neurodegenerative disorders are illnesses that involve the death of certain parts of the brain. Neurodegeneration or neuron death is the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons which includes disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease etc. In the United States, near about 60,000 cases of Parkinson’s disease are diagnosed per year.
NEUROPATHOLOGY AND APPLIED NEUROBIOLOGY
Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology is a peer-reviewed medical journal in the field of neuropathology. Neuropathology is the study of disease of nervous system tissues. In addition to examining central nervous system tissue, the neuropathologist usually is given the task of examining muscle & peripheral nerve biopsies as well. Neurobiology is the study of cells of the nervous system and the organization of these cells into functional circuits that process information and mediate the behaviour.
NEUROPSYCHIATRY
Neuropsychiatry is an integrative, collaborative discipline that arrangements with the psychiatric aspects of neurological disorders. In science, neuropsychiatry supports the field of neuroscience and is utilized to better comprehend the neurological underpinnings of the psychiatric and neurologic diseases and to analyze the treatment and care of people with neurological conditions, especially those that influence conduct.
NEUROCHEMISTRY
Neurochemistry alludes to the synthetic procedures that happen in the cerebrum and sensory system. There are two broad categories of chemistry in nerve systems that are important. The first is the chemistry that generates electrical signals which propagate along with nerve cells. The key chemicals involved in these signals are sodium and potassium ions. To see how they give rise to a signal, one must first look at a nerve cell that is at rest.
GERIATRIC NEUROLOGY
Geriatric neurology is the branch of medicine that studies neurologic disorders in elderly. The subspecialty of Geriatric neurology is defined by its expertise in the diagnosis, treatment, and care of neurological conditions that affect elderly and by its unique body of knowledge regarding the aging nervous system, its vulnerability to specific neurological disorders, and its influence on the prevalence and expression of neurological disease.
ALZHEIMER’S, DEMENTIA AND EPILEPSY
Alzheimer disease, the degenerative brain disorder that develops in mid-to-late adulthood. It results in a progressive and irreversible decline in memory and a deterioration of various other cognitive abilities. The disease is characterized by the destruction of nerve cells and neural connections in the cerebral cortex of the brain and by a significant loss of brain mass.
Dementia is a broad description which includes many different symptoms, including memory loss, word-finding difficulties, impaired judgment, and problems with day-to-day activities, which are caused by injury or loss of brain cells (neurons).
Epilepsy is a condition in which a person has repetitive seizures. A seizure is characterized as an abnormal, disorderly discharging of the brain's nerve cells, resulting in a temporary disturbance of motor, sensory, or mental function. The term epilepsy says nothing about the type of seizure or cause of the seizure, only that the seizures happen again and again.
NEURAL CODING
Neural coding means the concentration, identification, pleasurable and un pleasurable value of tastans which are represented in the form of action potential. It is of two types encoding and decoding. The map from stimuli to response is called as encoding whereas response to stimuli is called as decoding. It implies the connection between the response and the stimuli.
NEUROREHABILITATION
Neurorehabilitation intercessions have detonated since the year 2000, in parallel with a move in the worldview of neurologic care. In the mid-twentieth century, we got some distance from the supposition that the impact of mental damage, for example, a stroke on capacity, movement, and cooperation is perpetual and turned out to be progressively mindful of the cerebrum's regenerative potential, and additionally unique cerebrum rearrangement, months and even numerous years after the fact. Neurorehabilitation scientists pushed for translational research to define the permissive conditions under which optimal brain change and recovery occurs
NEUROCARDIOLOGY
Neurocardiology is the study of the neurophysiological, neurological and neuroanatomical aspects of cardiology, including especially the neurological origins of cardiac disorders. The neurocardiac pivot connects the cardiovascular and sensory systems to physiological issues. Clinical issues in Neurocardiology include neurogenic stress cardiomyopathy, cardiovascular findings in patients with primary neurological disease, neurologic sequelae of cardiac and thoracic surgery and cardiac interventions and hypoxic-ischemic brain injury.
The global neurology devices market is valued at XX million US$ in 2018 is expected to reach 19,914.7 million US$ by the end of 2025, growing at a CAGR of 8.3% during 2019-2025.
Neurological devices help to diagnose, prevent, and treat a variety of neurological disorders and conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, major depression, epilepsy, spinal cord injury, and traumatic brain injury. Neurological devices help to restore hearing and sight and provide the increased function for those with limb loss or congenital limb differences. Some of the neurological devices include neurodiagnostics, neurointerventional, and neurostimulation devices.
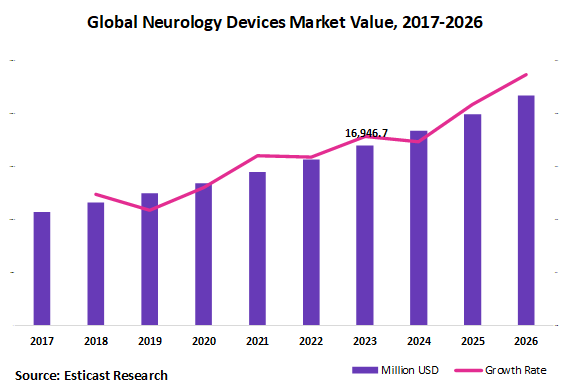
Global Neuroscience industry demand was worth USD 24.09 Billion in 2013 and is anticipated to reach above USD 30.80 billion by 2020. Rising investment in R&D resulting in the development of numerous products in the neuroinformatics coupled with adequate funding from the government are key factors that drive growth in this market.
Neuro-informatics involves designing and developing efficient tools and algorithms that can augment the performance of structural and functional mapping. Global Neuroscience market is expected to grow at CAGR of 2.9% over the next seven years.
As per the BCC report, the global market for neurological disease treatment and medication was worth $12.6 billion in 2006 and will reach $14 billion by 2007. At a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.6%, the global market will be worth almost $24.3 billion by 2012.
Drugs for multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease control approximately 99% of the total market share. Medications for multiple sclerosis are just over 35% greater than the market share of medication for Alzheimer's disease, despite the fact that there are far fewer patients with MS. As AD drugs become more prevalent, the shares of the market could change dramatically.
Report Scope
This report contains:
-
An analysis of the trends in drug discovery and development for the neurodegenerative disorders
-
An overview of the global neurological disorders treatment market which provides definitions and a structure for the industry
-
Provides details for the treatment markets of specific diseases such as Alzheimer's, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, muscular dystrophy, and other, rarer neurological disorders
-
Offers a detailed analysis of patents as well as important technological developments
-
A review of government regulations
-
Profiles the most important companies in the industry today.
Why Singapore??
SINGAPORE, called “the LION city,” becomes a favourite vacation spot due to the fact it's miles a international city and is a densely populated island with tropical vegetation, parks and gardens. Singapore is a international trade, finance and delivery hub.
Tourist attraction:
Sentosa, Singapore Flyer, Universal Studios Singapore, Night Safari Singapore, Singapore Botanic Gardens, Jurong Bird Park, Singapore Zoo, Sri Mariamman Temple, Pulau Hantu, Peranakan Museum.
Target Audience:
-
Industry - 21%
-
Student - 17%
-
Academia - 42%
-
Government - 11%
-
Others - 9%
Societies Associated with Neurological Research
-
Mental health Association in Maryland
-
Society for Mental Health Research
-
American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
-
Australian Clinical Psychology Association
-
American Association of Neurological Surgeons
-
World Psychiatry Association
-
American Psychiatric Association
-
European Psychiatric Association
Members Associated with Neurological Research
-
Neurologists
-
Psychologists
-
Neurosurgeons
-
Neuro Researchers
-
Students
-
Neuro Engineers
Top Neuroscience Universities in Singapore
-
National University of Singapore
-
Quintessential Education
-
UFC GYM Singapore Flagship Outlet
-
Nanyang Technological University
-
Duke-NUS Medical School
-
Department of Anatomy, NUS
-
National Neuroscience Institute
-
Dean's Office, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine
Top Neurology Universities in Globe
-
Leiden University
-
Keele University
-
Plymouth University
-
University of Toledo
-
University of Sheffield
-
University of Birmingham



